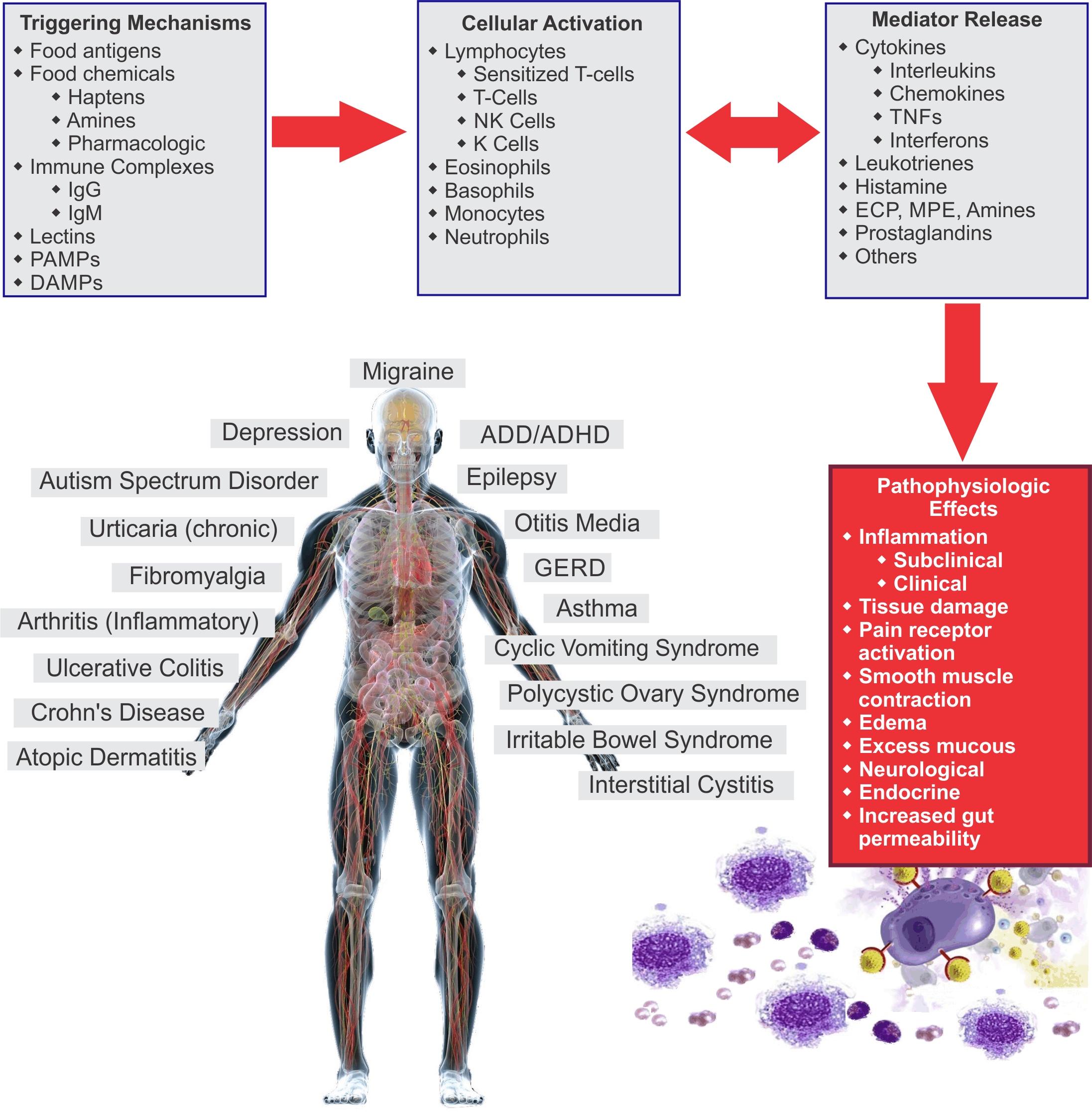
Sensitivities are complex non-allergic, non-celiac inflammatory reactions that can involve both innate and adaptive immune pathways. Various triggering mechanisms trigger reactions in white cells leading to the release of proinflammatory and proalgesic mediators, such as cytokines, leukotrienes, and prostaglandins. Mediator release and cellular reactivity ultimately results in subclinical and clinical inflammatory effects manifesting in a variety of clinical conditions and symptoms.